Chaos Mesh Workflow erstellen
Diese Seite wurde von PageTurner AI übersetzt (Beta). Nicht offiziell vom Projekt unterstützt. Fehler gefunden? Problem melden →
Einführung in Chaos Mesh Workflow
Bei der Nutzung von Chaos Mesh zur Simulation realer Systemfehler ist kontinuierliche Validierung essenziell. Statt einzelner Chaos-Injektionen können Sie auf der Chaos Mesh-Plattform eine Reihe von Fehlerszenarien aufbauen.
Hierfür bietet Chaos Mesh die integrierte Workflow-Engine "Chaos Mesh Workflow". Mit dieser Engine lassen sich verschiedene Chaos-Experimente seriell oder parallel ausführen, um produktionsnahe Fehler zu simulieren.
Aktuell unterstützt Chaos Mesh Workflow folgende Funktionen:
-
Serielle Orchestrierung
-
Parallele Orchestrierung
-
Benutzerdefinierte Tasks
-
Bedingte Verzweigung
Typische Anwendungsszenarien:
-
Parallele Injektion mehrerer NetworkChaos-Fehler zur Simulation komplexer Webumgebungen
-
Serielle Ausführung von Health Checks mit bedingter Verzweigung für nachfolgende Schritte
Das Design von Chaos Mesh Workflow ist teilweise von Argo Workflows inspiriert. Bei Erfahrung mit Argo Workflows finden Sie sich schnell zurecht.
Weitere Workflow-Beispiele finden Sie im Chaos Mesh GitHub-Repository.
Workflow mit Chaos Dashboard erstellen
Schritt 1: Chaos Dashboard öffnen
Klicken Sie auf NEW WORKFLOW.
Schritt 2: Workflow-Grunddaten konfigurieren

Schritt 3: Workflow-Knoten konfigurieren
-
Wählen Sie unter Choose task type den gewünschten Aufgabentyp.
In diesem Beispiel wird der Typ "Single" ausgewählt.
HinweisChaos Dashboard erstellt automatisch einen seriellen "entry"-Knoten als Workflow-Startpunkt.
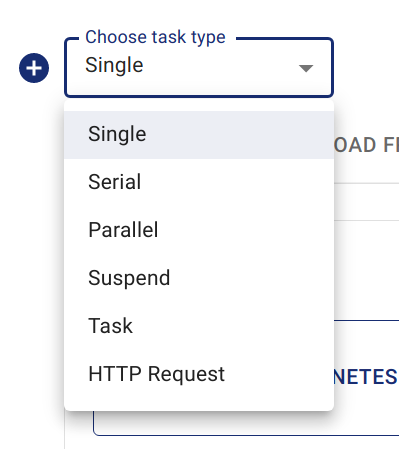
Aufgabentyp auswählen -
Geben Sie die Experimentdaten ein.
Die Konfiguration entspricht der Erstellung normaler Chaos-Experimente. Beispiel: Einrichten eines "POD KILL"-PodChaos mit dem Namen
kill-nginx.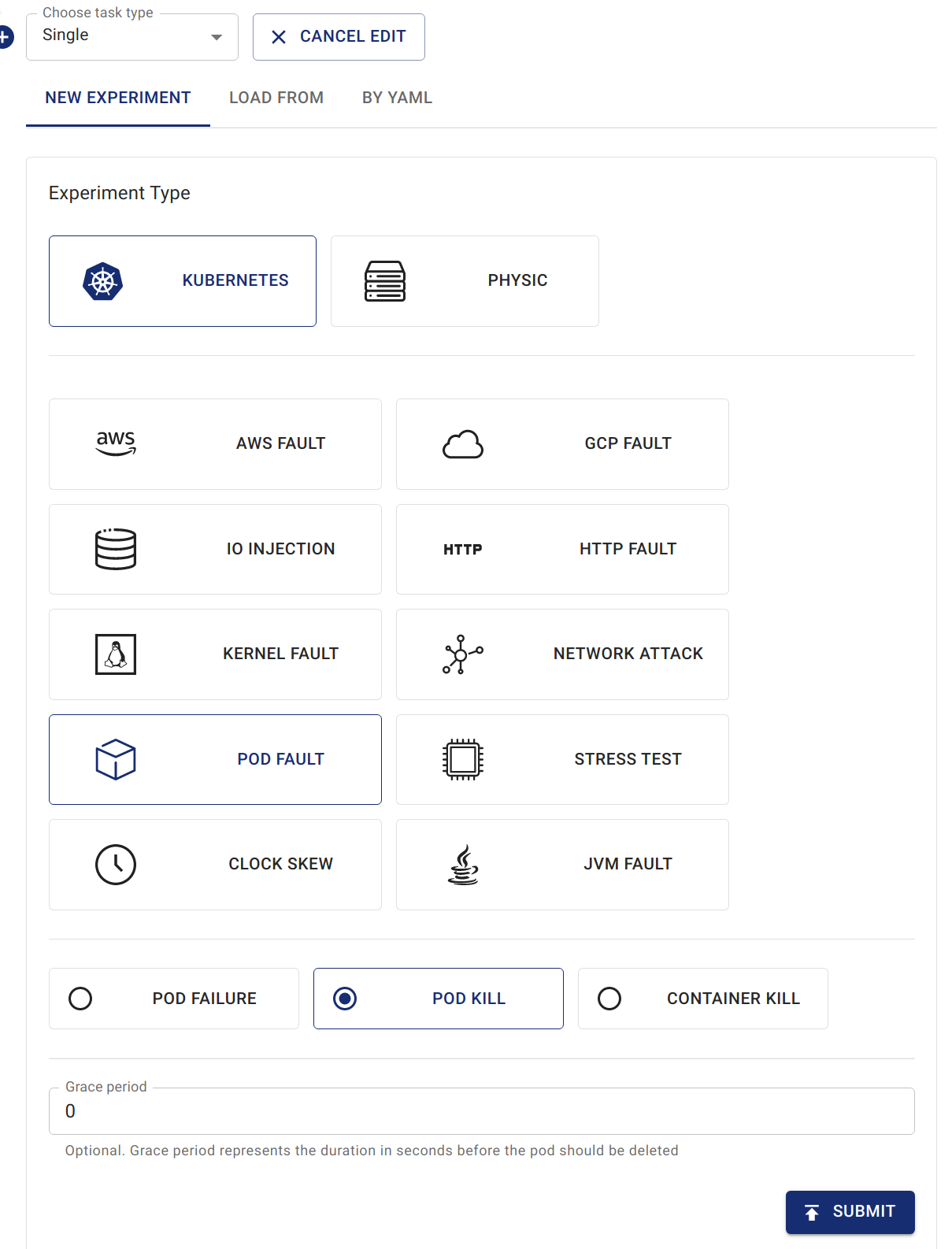
Podkill im Workflow erstellen
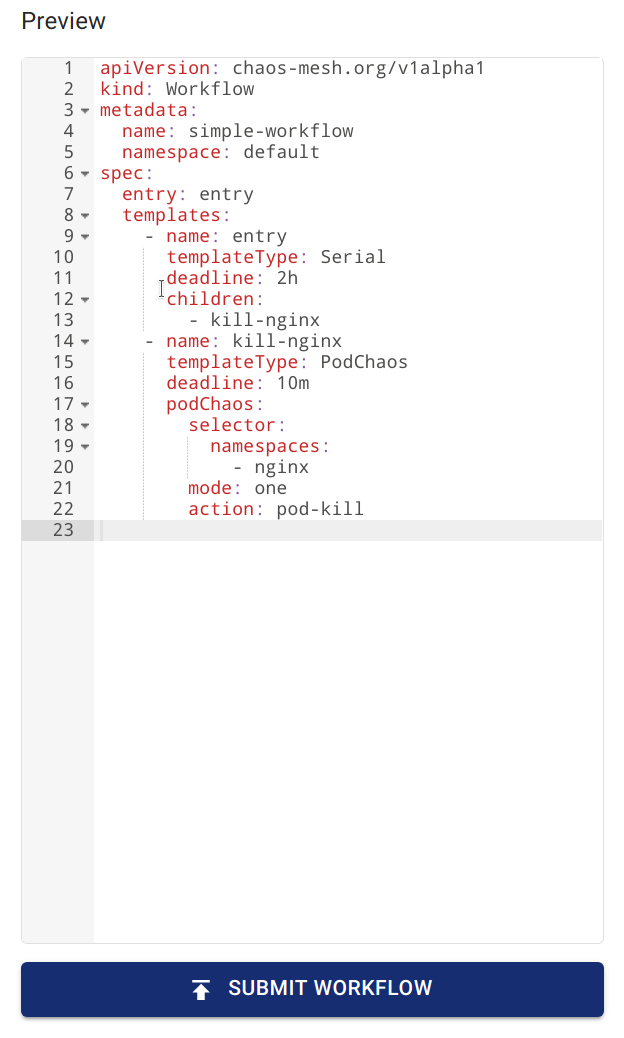
Schritt 4: Workflow bereitstellen
Überprüfen Sie die Workflow-Definition via Preview und klicken Sie auf SUBMIT WORKFLOW zur Erstellung.
Workflow per YAML-Datei und kubectl erstellen
Wie Chaos-Objekte existieren Workflows als Kubernetes-CRDs. Erstellen Sie sie mit kubectl create -f <workflow.yaml>. Beispielbefehl für lokale YAML-Datei:
kubectl create -f <workflow.yaml>
Erstellung mit Netzwerk-YAML-Datei:
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/master/examples/workflow/serial.yaml
Beispiel einer Workflow-YAML-Datei mit Injektion von StressChaos, NetworkChaos und PodChaos:
apiVersion: chaos-mesh.org/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
name: try-workflow-parallel
spec:
entry: the-entry
templates:
- name: the-entry
templateType: Parallel
deadline: 240s
children:
- workflow-stress-chaos
- workflow-network-chaos
- workflow-pod-chaos-schedule
- name: workflow-network-chaos
templateType: NetworkChaos
deadline: 20s
networkChaos:
direction: to
action: delay
mode: all
selector:
labelSelectors:
'app': 'hello-kubernetes'
delay:
latency: '90ms'
correlation: '25'
jitter: '90ms'
- name: workflow-pod-chaos-schedule
templateType: Schedule
deadline: 40s
schedule:
schedule: '@every 2s'
type: 'PodChaos'
podChaos:
action: pod-kill
mode: one
selector:
labelSelectors:
'app': 'hello-kubernetes'
- name: workflow-stress-chaos
templateType: StressChaos
deadline: 20s
stressChaos:
mode: one
selector:
labelSelectors:
'app': 'hello-kubernetes'
stressors:
cpu:
workers: 1
load: 20
options: ['--cpu 1', '--timeout 600']
Im YAML-Template definiert templates die Experimentschritte. Das entry-Feld legt den Workflow-Startpunkt bei der Ausführung fest.
Jedes Element in templates repräsentiert einen Workflow-Schritt. Beispiel:
name: the-entry
templateType: Parallel
deadline: 240s
children:
- workflow-stress-chaos
- workflow-network-chaos
- workflow-pod-chaos
templateType: Parallel definiert parallele Knotenausführung. deadline: 240s setzt ein 240-Sekunden-Timeout für parallele Experimente. children listet parallel auszuführende Template-Namen.
Beispiel:
name: workflow-pod-chaos
templateType: PodChaos
deadline: 40s
podChaos:
action: pod-kill
mode: one
selector:
labelSelectors:
'app': 'hello-kubernetes'
templateType: PodChaos bedeutet, dass der Knotentyp PodChaos-Experimente ist. deadline: 40s gibt an, dass das aktuelle Chaos-Experiment 40 Sekunden dauert. podChaos ist die Definition des PodChaos-Experiments.
Die Erstellung eines Workflows per YAML-Datei und kubectl bietet maximale Flexibilität. Sie können parallele oder serielle Abläufe verschachteln, um komplexe Orchestrierungen zu definieren und sogar bedingte Verzweigungen für Schleifen-Effekte nutzen.
Feldbeschreibung
Workflow-Feldbeschreibung
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default value | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | string | Declares the entry of the workflow. Its value is a name of a template. | None | Yes | |
| templates | []Template | Declares the behavior of each step executable in the workflow. See Template field description for details. | None | Yes |
Template-Feldbeschreibung
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default value | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | The name of the template, which needs to meet the DNS-1123 requirements. | None | Yes | any-name |
| type | string | Type of template. Value options are Task, Serial, Parallel, Suspend, Schedule, AWSChaos, DNSChaos, GCPChaos, HTTPChaos, IOChaos, JVMChaos, KernelChaos, NetworkChaos, PodChaos, StressChaos, and TimeChaos, StatusCheck. | None | Yes | PodChaos |
| deadline | string | The duration of the template. | None | No | '5m30s' |
| children | []string | Declares the subtasks under this template. You need to configure this field when the type is Serial or Parallel. | None | No | ["any-chaos-1", "another-serial-2", "any-shcedue"] |
| task | Task | Configures the customized task. You need to configure this field when the type is Task. See the Task field description for details. | None | No | |
| conditionalBranches | []ConditionalBranch | Configures the conditional branch which executes after customized task. You need to configure this field when the type is Task. See the Conditional branch field description for details. | None | No | |
| awsChaos | object | Configures AWSChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is AWSChaos. See the Simulate AWS Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| dnsChaos | object | Configures DNSChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is DNSChaos. See the Simulate DNS Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| gcpChaos | object | Configures GCPChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is GCPChaos.See the Simulation GCP Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| httpChaos | object | Configures HTTPChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is HTTPChaos. See the Simulate HTTP Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| ioChaos | object | Configure IOChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is IOChaos. See the Simulate File I/O Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| jvmChaos | object | Configures JVMChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is JVMChaos. See the Simulate JVM Application Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| kernelChaos | object | Configure KernelChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is KernelChaos. See the Simulate Kernel Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| networkChaos | object | Configures NetworkChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is NetworkChaos. See the Simulate Network Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| podChaos | object | Configures PodChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is PodChaos. See the Simulate Pod Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| stressChaos | object | Configures StressChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is StressChaos. See the Simulate Heavy Stress on Kubernetes document for details. | None | No | |
| timeChaos | object | Configures TimeChaos. You need to configure this field when the type is TimeChaos. See the SImulate Time Faults document for details. | None | No | |
| schedule | object | Configures Schedule. You need to configure this field when the type is Schedule. See the Define Scheduling Rules document for details. | None | No | |
| statusCheck | object | Configures StatusCheck. You need to configure this field when the type is StatusCheck. See the StatusCheck in Workflow document for details. | None | No | |
| abortWithStatusCheck | bool | Configures whether abort the Workflow when StatusCheck is failed. You can configure this field when the type is StatusCheck. | false | No | true |
Bei der Erstellung eines Chaos-Experiments mit Zeitdauer im Workflow muss die Dauer im äußeren deadline-Feld angegeben werden – nicht im duration-Feld des Chaos-Experiments.
Task-Feldbeschreibung
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default value | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| container | object | Defines a customized task container. See Container field description for details. | None | No | |
| volumes | array | If you need to mount a volume in a customized task container, you need to declare the volume in this field. For the detailed definition of a volume, see the Kubernetes documentation - corev1.Volume. | None | No |
ConditionalBranch-Feldbeschreibung
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default value | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| target | string | The name of the template to be executed by the current conditional branch. | None | Yes | another-chaos |
| expression | string | The type is a boolean expression. When a customized task is completed and the expression value is true, the current condition branch is executed. When this value is not set, the conditional branch will be executed directly after the customized task is completed. | None | No | exitCode == 0 |
Derzeit stehen in expression zwei Kontextvariablen zur Verfügung:
-
exitCodegibt den Exit-Code eines benutzerdefinierten Tasks an. -
stdoutrepräsentiert die Standardausgabe eines benutzerdefinierten Tasks.
Weitere Kontextvariablen folgen in späteren Releases.
Die Syntax für expression-Ausdrücke ist in diesem Dokument beschrieben.
Container-Feldbeschreibung
Die Tabelle zeigt nur häufig genutzte Felder. Vollständige Felddefinitionen finden Sie in der Kubernetes-Dokumentation - core1.Container.
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default value | Required | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Container name | None | Yes | task |
| image | string | Image name | None | Yes | busybox:latest |
| command | []string | Container commands | None | No | ["wget", "-q", "http://httpbin.org/status/201"] |