在 Kubernetes 中实施混沌工程:Chaos Mesh 原理分析与控制平面开发
本页面由 PageTurner AI 翻译(测试版)。未经项目官方认可。 发现错误? 报告问题 →
Chaos Mesh 是一款基于 Kubernetes(K8s)自定义资源定义(CRD)构建的开源云原生混沌工程平台。它能够模拟多种类型的故障,并具备强大的故障场景编排能力。通过 Chaos Mesh,您可以便捷地在开发、测试和生产环境中模拟各类异常情况,从而发现系统中的潜在问题。
本文将深入探讨 Kubernetes 集群中的混沌工程实践,通过源码分析解读 Chaos Mesh 的核心特性,并配合代码示例讲解如何开发 Chaos Mesh 控制平面。
如果您尚未熟悉 Chaos Mesh,建议先阅读 Chaos Mesh 文档 了解其基础架构。
本文涉及的测试代码请参见 GitHub 仓库 mayocream/chaos-mesh-controlpanel-demo。
Chaos Mesh 如何制造混沌
Chaos Mesh 堪称 Kubernetes 混沌工程的瑞士军刀。本节将解析其实现机制。
特权模式
Chaos Mesh 通过 Kubernetes 中的特权容器制造故障。Chaos Daemon 的 Pod 以 DaemonSet 形式运行,并通过 Pod 的安全上下文为容器运行时添加额外的 能力。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
spec:
template:
metadata: ...
spec:
containers:
- name: chaos-daemon
securityContext:
{{- if .Values.chaosDaemon.privileged }}
privileged: true
capabilities:
add:
- SYS_PTRACE
{{- else }}
capabilities:
add:
- SYS_PTRACE
- NET_ADMIN
- MKNOD
- SYS_CHROOT
- SYS_ADMIN
- KILL
# CAP_IPC_LOCK is used to lock memory
- IPC_LOCK
{{- end }}
Linux 能力机制授予容器创建和访问 /dev/fuse 用户空间文件系统(FUSE)管道的权限。FUSE 作为 Linux 用户态文件系统接口,允许非特权用户无需修改内核代码即可创建自有文件系统。
根据 GitHub 上的 pull request #1109,DaemonSet 程序通过 cgo 调用 Linux makedev 函数创建 FUSE 管道。
// #include <sys/sysmacros.h>
// #include <sys/types.h>
// // makedev is a macro, so a wrapper is needed
// dev_t Makedev(unsigned int maj, unsigned int min) {
// return makedev(maj, min);
// }
// EnsureFuseDev ensures /dev/fuse exists. If not, it will create one
func EnsureFuseDev() {
if _, err := os.Open("/dev/fuse"); os.IsNotExist(err) {
// 10, 229 according to https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/admin-guide/devices.txt
fuse := C.Makedev(10, 229)
syscall.Mknod("/dev/fuse", 0o666|syscall.S_IFCHR, int(fuse))
}
}
在 pull request #1453 中,Chaos Daemon 默认启用特权模式,即在容器 SecurityContext 中设置 privileged: true。
终止 Pod
PodKill、PodFailure 和 ContainerKill 同属 PodChaos 类别。其中 PodKill 会随机终止 Pod,通过调用 API 服务器发送终止指令实现。
import (
"context"
v1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
"sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client"
)
type Impl struct {
client.Client
}
func (impl *Impl) Apply(ctx context.Context, index int, records []*v1alpha1.Record, obj v1alpha1.InnerObject) (v1alpha1.Phase, error) {
...
err = impl.Get(ctx, namespacedName, &pod)
if err != nil {
// TODO: handle this error
return v1alpha1.NotInjected, err
}
err = impl.Delete(ctx, &pod, &client.DeleteOptions{
GracePeriodSeconds: &podchaos.Spec.GracePeriod, // PeriodSeconds has to be set specifically
})
...
return v1alpha1.Injected, nil
}
GracePeriodSeconds 参数允许 Kubernetes 强制终止 Pod。例如需立即删除 Pod 时,可使用 kubectl delete pod --grace-period=0 --force 命令。
PodFailure 通过修补 Pod 对象资源,将容器镜像替换为错误镜像。该操作仅修改 containers 和 initContainers 的 image 字段,这是因为 Pod 的大部分元数据不可变更。详见 Pod 更新与替换。
func (impl *Impl) Apply(ctx context.Context, index int, records []*v1alpha1.Record, obj v1alpha1.InnerObject) (v1alpha1.Phase, error) {
...
pod := origin.DeepCopy()
for index := range pod.Spec.Containers {
originImage := pod.Spec.Containers[index].Image
name := pod.Spec.Containers[index].Name
key := annotation.GenKeyForImage(podchaos, name, false)
if pod.Annotations == nil {
pod.Annotations = make(map[string]string)
}
// If the annotation is already existed, we could skip the reconcile for this container
if _, ok := pod.Annotations[key]; ok {
continue
}
pod.Annotations[key] = originImage
pod.Spec.Containers[index].Image = config.ControllerCfg.PodFailurePauseImage
}
for index := range pod.Spec.InitContainers {
originImage := pod.Spec.InitContainers[index].Image
name := pod.Spec.InitContainers[index].Name
key := annotation.GenKeyForImage(podchaos, name, true)
if pod.Annotations == nil {
pod.Annotations = make(map[string]string)
}
// If the annotation is already existed, we could skip the reconcile for this container
if _, ok := pod.Annotations[key]; ok {
continue
}
pod.Annotations[key] = originImage
pod.Spec.InitContainers[index].Image = config.ControllerCfg.PodFailurePauseImage
}
err = impl.Patch(ctx, pod, client.MergeFrom(&origin))
if err != nil {
// TODO: handle this error
return v1alpha1.NotInjected, err
}
return v1alpha1.Injected, nil
}
触发故障的默认容器镜像是 gcr.io/google-containers/pause:latest。
PodKill 和 PodFailure 通过 Kubernetes API 服务器控制 Pod 生命周期,而 ContainerKill 则通过运行在集群节点上的 Chaos Daemon 实现。ContainerKill 由 Chaos Controller Manager 调用客户端发起 gRPC 请求至 Chaos Daemon。
func (b *ChaosDaemonClientBuilder) Build(ctx context.Context, pod *v1.Pod) (chaosdaemonclient.ChaosDaemonClientInterface, error) {
...
daemonIP, err := b.FindDaemonIP(ctx, pod)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
builder := grpcUtils.Builder(daemonIP, config.ControllerCfg.ChaosDaemonPort).WithDefaultTimeout()
if config.ControllerCfg.TLSConfig.ChaosMeshCACert != "" {
builder.TLSFromFile(config.ControllerCfg.TLSConfig.ChaosMeshCACert, config.ControllerCfg.TLSConfig.ChaosDaemonClientCert, config.ControllerCfg.TLSConfig.ChaosDaemonClientKey)
} else {
builder.Insecure()
}
cc, err := builder.Build()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return chaosdaemonclient.New(cc), nil
}
当 Chaos Controller Manager 向 Chaos Daemon 发送指令时,会根据 Pod 信息创建对应的客户端。例如,要控制某节点上的 Pod,会通过获取该 Pod 所在节点的 ClusterIP 来创建客户端。若存在传输层安全(TLS)证书配置,Controller Manager 还会为客户端添加 TLS 证书。
Chaos Daemon 启动时若检测到 TLS 证书,会加载证书启用 gRPCS 协议。TLS 配置选项 RequireAndVerifyClientCert 用于决定是否启用双向 TLS(mTLS)认证。
func newGRPCServer(containerRuntime string, reg prometheus.Registerer, tlsConf tlsConfig) (*grpc.Server, error) {
...
if tlsConf != (tlsConfig{}) {
caCert, err := ioutil.ReadFile(tlsConf.CaCert)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
caCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
caCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(caCert)
serverCert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair(tlsConf.Cert, tlsConf.Key)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
creds := credentials.NewTLS(&tls.Config{
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{serverCert},
ClientCAs: caCertPool,
ClientAuth: tls.RequireAndVerifyClientCert,
})
grpcOpts = append(grpcOpts, grpc.Creds(creds))
}
s := grpc.NewServer(grpcOpts...)
grpcMetrics.InitializeMetrics(s)
pb.RegisterChaosDaemonServer(s, ds)
reflection.Register(s)
return s, nil
}
Chaos Daemon 提供以下可调用的 gRPC 接口:
// ChaosDaemonClient is the client API for ChaosDaemon service.
//
// For semantics around ctx use and closing/ending streaming RPCs, please refer to https://godoc.org/google.golang.org/grpc#ClientConn.NewStream.
type ChaosDaemonClient interface {
SetTcs(ctx context.Context, in *TcsRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*empty.Empty, error)
FlushIPSets(ctx context.Context, in *IPSetsRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*empty.Empty, error)
SetIptablesChains(ctx context.Context, in *IptablesChainsRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*empty.Empty, error)
SetTimeOffset(ctx context.Context, in *TimeRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*empty.Empty, error)
RecoverTimeOffset(ctx context.Context, in *TimeRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*empty.Empty, error)
ContainerKill(ctx context.Context, in *ContainerRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*empty.Empty, error)
ContainerGetPid(ctx context.Context, in *ContainerRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*ContainerResponse, error)
ExecStressors(ctx context.Context, in *ExecStressRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*ExecStressResponse, error)
CancelStressors(ctx context.Context, in *CancelStressRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*empty.Empty, error)
ApplyIOChaos(ctx context.Context, in *ApplyIOChaosRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*ApplyIOChaosResponse, error)
ApplyHttpChaos(ctx context.Context, in *ApplyHttpChaosRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*ApplyHttpChaosResponse, error)
SetDNSServer(ctx context.Context, in *SetDNSServerRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*empty.Empty, error)
}
网络故障注入
从 pull request #41 可知,Chaos Mesh 通过调用 pbClient.SetNetem 将参数封装为请求,发送到目标节点的 Chaos Daemon 进行处理来实现网络故障注入。
下图为 2019 年网络故障注入的原始代码实现。随着项目演进,相关功能已分散至多个文件。
func (r *Reconciler) applyPod(ctx context.Context, pod *v1.Pod, networkchaos *v1alpha1.NetworkChaos) error {
...
pbClient := pb.NewChaosDaemonClient(c)
containerId := pod.Status.ContainerStatuses[0].ContainerID
netem, err := spec.ToNetem()
if err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = pbClient.SetNetem(ctx, &pb.NetemRequest{
ContainerId: containerId,
Netem: netem,
})
return err
}
在 pkg/chaosdaemon 包中可查看 Chaos Daemon 处理请求的具体逻辑。
func (s *Server) SetNetem(ctx context.Context, in *pb.NetemRequest) (*empty.Empty, error) {
log.Info("Set netem", "Request", in)
pid, err := s.crClient.GetPidFromContainerID(ctx, in.ContainerId)
if err != nil {
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.Internal, "get pid from containerID error: %v", err)
}
if err := Apply(in.Netem, pid); err != nil {
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.Internal, "netem apply error: %v", err)
}
return &empty.Empty{}, nil
}
// Apply applies a netem on eth0 in pid related namespace
func Apply(netem *pb.Netem, pid uint32) error {
log.Info("Apply netem on PID", "pid", pid)
ns, err := netns.GetFromPath(GenNetnsPath(pid))
if err != nil {
log.Error(err, "failed to find network namespace", "pid", pid)
return errors.Trace(err)
}
defer ns.Close()
handle, err := netlink.NewHandleAt(ns)
if err != nil {
log.Error(err, "failed to get handle at network namespace", "network namespace", ns)
return err
}
link, err := handle.LinkByName("eth0") // TODO: check whether interface name is eth0
if err != nil {
log.Error(err, "failed to find eth0 interface")
return errors.Trace(err)
}
netemQdisc := netlink.NewNetem(netlink.QdiscAttrs{
LinkIndex: link.Attrs().Index,
Handle: netlink.MakeHandle(1, 0),
Parent: netlink.HANDLE_ROOT,
}, ToNetlinkNetemAttrs(netem))
if err = handle.QdiscAdd(netemQdisc); err != nil {
if !strings.Contains(err.Error(), "file exists") {
log.Error(err, "failed to add Qdisc")
return errors.Trace(err)
}
}
return nil
}
最终通过 vishvananda/netlink 库操作 Linux 网络接口完成任务。
由此可见,NetworkChaos 通过操纵 Linux 主机网络(包括 iptables、ipset 等工具)制造混沌环境。
在 Chaos Daemon 的 Dockerfile 中可见其依赖的 Linux 工具链:
RUN apt-get update && \
apt-get install -y tzdata iptables ipset stress-ng iproute2 fuse util-linux procps curl && \
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
压力测试
Chaos Daemon 同样实现 StressChaos 功能。Controller Manager 计算规则后,将任务发送至特定 Daemon。下图展示组装后的参数,这些参数会拼接为命令行参数附加到 stress-ng 命令中执行。
// Normalize the stressors to comply with stress-ng
func (in *Stressors) Normalize() (string, error) {
stressors := ""
if in.MemoryStressor != nil && in.MemoryStressor.Workers != 0 {
stressors += fmt.Sprintf(" --vm %d --vm-keep", in.MemoryStressor.Workers)
if len(in.MemoryStressor.Size) != 0 {
if in.MemoryStressor.Size[len(in.MemoryStressor.Size)-1] != '%' {
size, err := units.FromHumanSize(string(in.MemoryStressor.Size))
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
stressors += fmt.Sprintf(" --vm-bytes %d", size)
} else {
stressors += fmt.Sprintf(" --vm-bytes %s",
in.MemoryStressor.Size)
}
}
if in.MemoryStressor.Options != nil {
for _, v := range in.MemoryStressor.Options {
stressors += fmt.Sprintf(" %v ", v)
}
}
}
if in.CPUStressor != nil && in.CPUStressor.Workers != 0 {
stressors += fmt.Sprintf(" --cpu %d", in.CPUStressor.Workers)
if in.CPUStressor.Load != nil {
stressors += fmt.Sprintf(" --cpu-load %d",
*in.CPUStressor.Load)
}
if in.CPUStressor.Options != nil {
for _, v := range in.CPUStressor.Options {
stressors += fmt.Sprintf(" %v ", v)
}
}
}
return stressors, nil
}
服务端通过 Go 官方包 os/exec 处理函数执行命令,详见 pkg/chaosdaemon/stress_server_linux.go 文件。另存同名 darwin 后缀文件(*_darwin)是为避免程序在 macOS 运行时可能出现的错误。
代码使用 shirou/gopsutil 包获取 PID 进程状态,并读取 stdout/stderr 标准输出。这种处理模式也见于 hashicorp/go-plugin,且 go-plugin 的实现更为完善。
I/O 故障注入
Pull request #826 引入了无需 sidecar 注入的 IOChaos 新实现:通过 Chaos Daemon 借助 runc 容器的底层命令直接操作 Linux 命名空间,并运行 Rust 开发的 chaos-mesh/toda FUSE 程序注入容器 I/O 混沌。控制平面与 toda 之间采用 JSON-RPC 2.0 协议通信。
新版 IOChaos 实现方案无需修改 Pod 资源。当您定义 IOChaos 混沌实验时,系统会为选择器(selector)字段筛选出的每个 Pod 创建对应的 PodIoChaos 资源。PodIoChaos 通过 属主引用 与 Pod 建立关联,同时为其添加一组 终结器,确保 PodIoChaos 资源删除前完成资源释放。
// Apply implements the reconciler.InnerReconciler.Apply
func (r *Reconciler) Apply(ctx context.Context, req ctrl.Request, chaos v1alpha1.InnerObject) error {
iochaos, ok := chaos.(*v1alpha1.IoChaos)
if !ok {
err := errors.New("chaos is not IoChaos")
r.Log.Error(err, "chaos is not IoChaos", "chaos", chaos)
return err
}
source := iochaos.Namespace + "/" + iochaos.Name
m := podiochaosmanager.New(source, r.Log, r.Client)
pods, err := utils.SelectAndFilterPods(ctx, r.Client, r.Reader, &iochaos.Spec)
if err != nil {
r.Log.Error(err, "failed to select and filter pods")
return err
}
r.Log.Info("applying iochaos", "iochaos", iochaos)
for _, pod := range pods {
t := m.WithInit(types.NamespacedName{
Name: pod.Name,
Namespace: pod.Namespace,
})
// TODO: support chaos on multiple volume
t.SetVolumePath(iochaos.Spec.VolumePath)
t.Append(v1alpha1.IoChaosAction{
Type: iochaos.Spec.Action,
Filter: v1alpha1.Filter{
Path: iochaos.Spec.Path,
Percent: iochaos.Spec.Percent,
Methods: iochaos.Spec.Methods,
},
Faults: []v1alpha1.IoFault{
{
Errno: iochaos.Spec.Errno,
Weight: 1,
},
},
Latency: iochaos.Spec.Delay,
AttrOverrideSpec: iochaos.Spec.Attr,
Source: m.Source,
})
key, err := cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(&pod)
if err != nil {
return err
}
iochaos.Finalizers = utils.InsertFinalizer(iochaos.Finalizers, key)
}
r.Log.Info("commiting updates of podiochaos")
err = m.Commit(ctx)
if err != nil {
r.Log.Error(err, "fail to commit")
return err
}
r.Event(iochaos, v1.EventTypeNormal, utils.EventChaosInjected, "")
return nil
}
在 PodIoChaos 资源的控制器中,Controller Manager 将资源封装为参数,通过调用 Chaos Daemon 接口处理这些参数。
// Apply flushes io configuration on pod
func (h *Handler) Apply(ctx context.Context, chaos *v1alpha1.PodIoChaos) error {
h.Log.Info("updating io chaos", "pod", chaos.Namespace+"/"+chaos.Name, "spec", chaos.Spec)
...
res, err := pbClient.ApplyIoChaos(ctx, &pb.ApplyIoChaosRequest{
Actions: input,
Volume: chaos.Spec.VolumeMountPath,
ContainerId: containerID,
Instance: chaos.Spec.Pid,
StartTime: chaos.Spec.StartTime,
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
chaos.Spec.Pid = res.Instance
chaos.Spec.StartTime = res.StartTime
chaos.OwnerReferences = []metav1.OwnerReference{
{
APIVersion: pod.APIVersion,
Kind: pod.Kind,
Name: pod.Name,
UID: pod.UID,
},
}
return nil
}
pkg/chaosdaemon/iochaos_server.go 文件负责处理 IOChaos。该文件需将 FUSE 程序注入容器,如 GitHub 议题 #2305 所述,需执行 /usr/local/bin/nsexec -l- p /proc/119186/ns/pid -m /proc/119186/ns/mnt - /usr/local/bin/toda --path /tmp --verbose info 命令,使 toda 程序在 Pod 的相同命名空间下运行。
func (s *DaemonServer) ApplyIOChaos(ctx context.Context, in *pb.ApplyIOChaosRequest) (*pb.ApplyIOChaosResponse, error) {
...
pid, err := s.crClient.GetPidFromContainerID(ctx, in.ContainerId)
if err != nil {
log.Error(err, "error while getting PID")
return nil, err
}
args := fmt.Sprintf("--path %s --verbose info", in.Volume)
log.Info("executing", "cmd", todaBin+" "+args)
processBuilder := bpm.DefaultProcessBuilder(todaBin, strings.Split(args, " ")...).
EnableLocalMnt().
SetIdentifier(in.ContainerId)
if in.EnterNS {
processBuilder = processBuilder.SetNS(pid, bpm.MountNS).SetNS(pid, bpm.PidNS)
}
...
// Calls JSON RPC
client, err := jrpc.DialIO(ctx, receiver, caller)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
cmd := processBuilder.Build()
procState, err := s.backgroundProcessManager.StartProcess(cmd)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
...
}
以下代码示例构建了运行命令,这些命令本质上是 runc 的命名空间隔离实现:
// GetNsPath returns corresponding namespace path
func GetNsPath(pid uint32, typ NsType) string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%s/%d/ns/%s", DefaultProcPrefix, pid, string(typ))
}
// SetNS sets the namespace of the process
func (b *ProcessBuilder) SetNS(pid uint32, typ NsType) *ProcessBuilder {
return b.SetNSOpt([]nsOption{{
Typ: typ,
Path: GetNsPath(pid, typ),
}})
}
// Build builds the process
func (b *ProcessBuilder) Build() *ManagedProcess {
args := b.args
cmd := b.cmd
if len(b.nsOptions) > 0 {
args = append([]string{"--", cmd}, args...)
for _, option := range b.nsOptions {
args = append([]string{"-" + nsArgMap[option.Typ], option.Path}, args...)
}
if b.localMnt {
args = append([]string{"-l"}, args...)
}
cmd = nsexecPath
}
...
}
控制平面
Chaos Mesh 是遵循 Apache 2.0 协议的开源混沌工程系统。如前所述,它具备丰富的能力和良好的生态。维护团队基于该系统开发了 chaos-mesh/toda FUSE 组件、chaos-mesh/k8s_dns_chaos CoreDNS 混沌插件,以及基于伯克利包过滤器(BPF)的内核错误注入工具 chaos-mesh/bpfki。
接下来我将描述构建面向终端用户的混沌工程平台所需的服务器端代码。此实现仅为示例——并非最佳实践。若需了解实际平台的开发实践,可参考 Chaos Mesh 的 Dashboard。该项目采用 uber-go/fx 依赖注入框架和控制器运行时的管理器模式。
Chaos Mesh 核心特性
如下图所示 Chaos Mesh 工作流,我们需要实现向 Kubernetes API 发送 YAML 的服务器。Chaos Controller Manager 负责执行复杂的规则验证及向 Chaos Daemon 交付规则。若需将 Chaos Mesh 集成到自有平台,仅需对接创建 CRD 资源的流程。
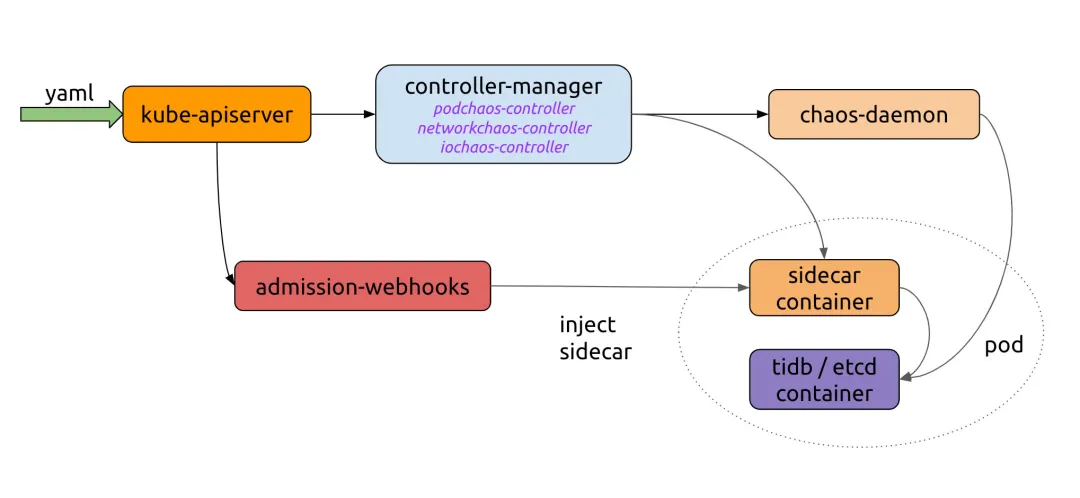
让我们查看 Chaos Mesh 官网的示例:
import (
"context"
"github.com/pingcap/chaos-mesh/api/v1alpha1"
"sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client"
)
func main() {
...
delay := &chaosv1alpha1.NetworkChaos{
Spec: chaosv1alpha1.NetworkChaosSpec{...},
}
k8sClient := client.New(conf, client.Options{ Scheme: scheme.Scheme })
k8sClient.Create(context.TODO(), delay)
k8sClient.Delete(context.TODO(), delay)
}
Chaos Mesh 为所有 CRD 提供对应的 API。我们使用 Kubernetes API Machinery SIG 开发的 controller-runtime 来简化与 Kubernetes API 的交互。
注入混沌
假设我们需通过程序创建 PodKill 资源。资源提交至 Kubernetes API Server 后,会经过 Chaos Controller Manager 的 验证准入控制器 进行数据校验。创建混沌实验时,若准入控制器验证输入数据失败,将向客户端返回错误。具体参数规范请参阅 使用 YAML 配置文件创建实验。
NewClient 创建 Kubernetes API 客户端,可参考以下示例:
package main
import (
"context"
"controlpanel"
"log"
"github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/api/v1alpha1"
"github.com/pkg/errors"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
)
func applyPodKill(name, namespace string, labels map[string]string) error {
cli, err := controlpanel.NewClient()
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "create client")
}
cr := &v1alpha1.PodChaos{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
GenerateName: name,
Namespace: namespace,
},
Spec: v1alpha1.PodChaosSpec{
Action: v1alpha1.PodKillAction,
ContainerSelector: v1alpha1.ContainerSelector{
PodSelector: v1alpha1.PodSelector{
Mode: v1alpha1.OnePodMode,
Selector: v1alpha1.PodSelectorSpec{
Namespaces: []string{namespace},
LabelSelectors: labels,
},
},
},
},
}
if err := cli.Create(context.Background(), cr); err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "create podkill")
}
return nil
}
运行程序的日志输出为:
I1021 00:51:55.225502 23781 request.go:665] Waited for 1.033116256s due to client-side throttling, not priority and fairness, request: GET:https://***
2021/10/21 00:51:56 apply podkill
使用 kubectl 查看 PodKill 资源状态:
$ k describe podchaos.chaos-mesh.org -n dev podkillvjn77
Name: podkillvjn77
Namespace: dev
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: chaos-mesh.org/v1alpha1
Kind: PodChaos
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2021-10-20T16:51:56Z
Finalizers:
chaos-mesh/records
Generate Name: podkill
Generation: 7
Resource Version: 938921488
Self Link: /apis/chaos-mesh.org/v1alpha1/namespaces/dev/podchaos/podkillvjn77
UID: afbb40b3-ade8-48ba-89db-04918d89fd0b
Spec:
Action: pod-kill
Grace Period: 0
Mode: one
Selector:
Label Selectors:
app: nginx
Namespaces:
dev
Status:
Conditions:
Reason:
Status: False
Type: Paused
Reason:
Status: True
Type: Selected
Reason:
Status: True
Type: AllInjected
Reason:
Status: False
Type: AllRecovered
Experiment:
Container Records:
Id: dev/nginx
Phase: Injected
Selector Key: .
Desired Phase: Run
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal FinalizerInited 6m35s finalizer Finalizer has been inited
Normal Updated 6m35s finalizer Successfully update finalizer of resource
Normal Updated 6m35s records Successfully update records of resource
Normal Updated 6m35s desiredphase Successfully update desiredPhase of resource
Normal Applied 6m35s records Successfully apply chaos for dev/nginx
Normal Updated 6m35s records Successfully update records of resource
控制平面还需查询和获取混沌资源,以便平台用户查看所有混沌实验的执行状态并进行管理。为此,我们可以调用 REST API 发送 Get 或 List 请求。但在实际应用中需注意细节:我们公司发现每次控制器请求全量资源数据时,Kubernetes API 服务器的负载都会显著增加。
建议阅读日文教程《如何使用 controller-runtime 客户端》。即使不懂日语,通过阅读源码也能获得许多实用细节:controller runtime 默认会从多个位置自动读取 kubeconfig、命令行标志、环境变量以及 Pod 内自动挂载的服务账号。armosec/kubescape 的PR #21 就运用了此特性。该教程还涵盖分页查询、对象更新和覆盖等常规操作,其详细程度在英文教程中罕见。
以下是 Get 和 List 请求的示例:
package controlpanel
import (
"context"
"github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/api/v1alpha1"
"github.com/pkg/errors"
"sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client"
)
func GetPodChaos(name, namespace string) (*v1alpha1.PodChaos, error) {
cli := mgr.GetClient()
item := new(v1alpha1.PodChaos)
if err := cli.Get(context.Background(), client.ObjectKey{Name: name, Namespace: namespace}, item); err != nil {
return nil, errors.Wrap(err, "get cr")
}
return item, nil
}
func ListPodChaos(namespace string, labels map[string]string) ([]v1alpha1.PodChaos, error) {
cli := mgr.GetClient()
list := new(v1alpha1.PodChaosList)
if err := cli.List(context.Background(), list, client.InNamespace(namespace), client.MatchingLabels(labels)); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return list.Items, nil
}
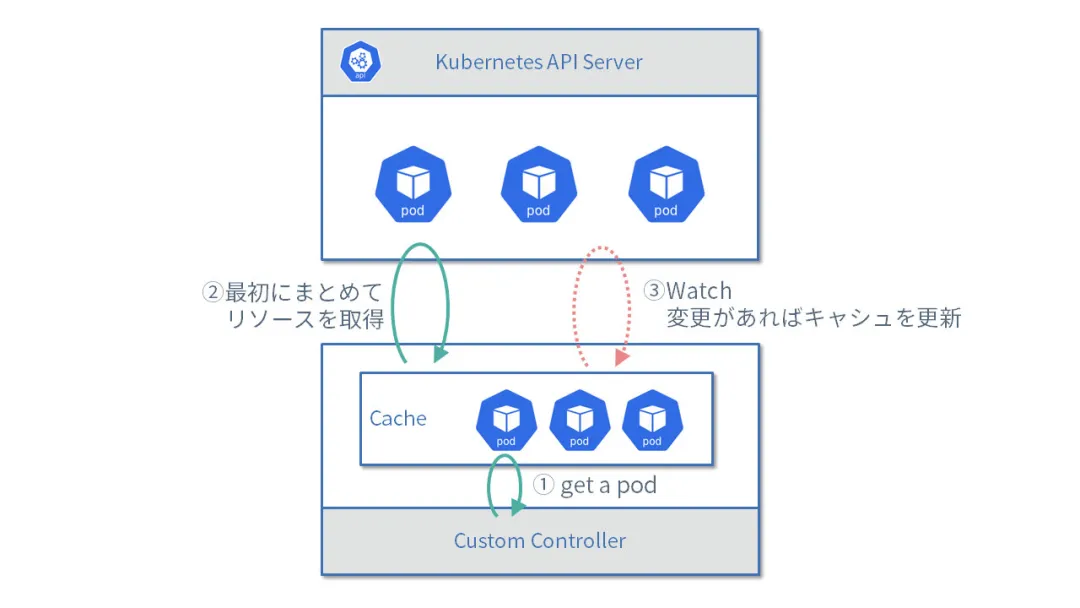
此示例使用管理器模式,可避免缓存机制重复拉取大量数据。下面的图展示了工作流程:
-
获取 Pod
-
首次获取
List请求的完整数据 -
监视数据变化时更新缓存
编排混沌实验
容器运行时接口(CRI)虽提供强大的底层隔离能力保障容器稳定运行,但更复杂、可扩展的场景需要容器编排能力。Chaos Mesh 也提供 Schedule 和 Workflow 功能:Schedule 可按预设 Cron 时间定时/间隔触发故障,Workflow 则能像 Argo Workflows 那样编排多个故障测试。
Chaos Controller Manager 已承担大部分工作,控制平面主要管理这些 YAML 资源,您只需考虑向最终用户提供哪些功能。
平台功能设计
下图展示的 Chaos Mesh 仪表盘可启发平台功能规划:
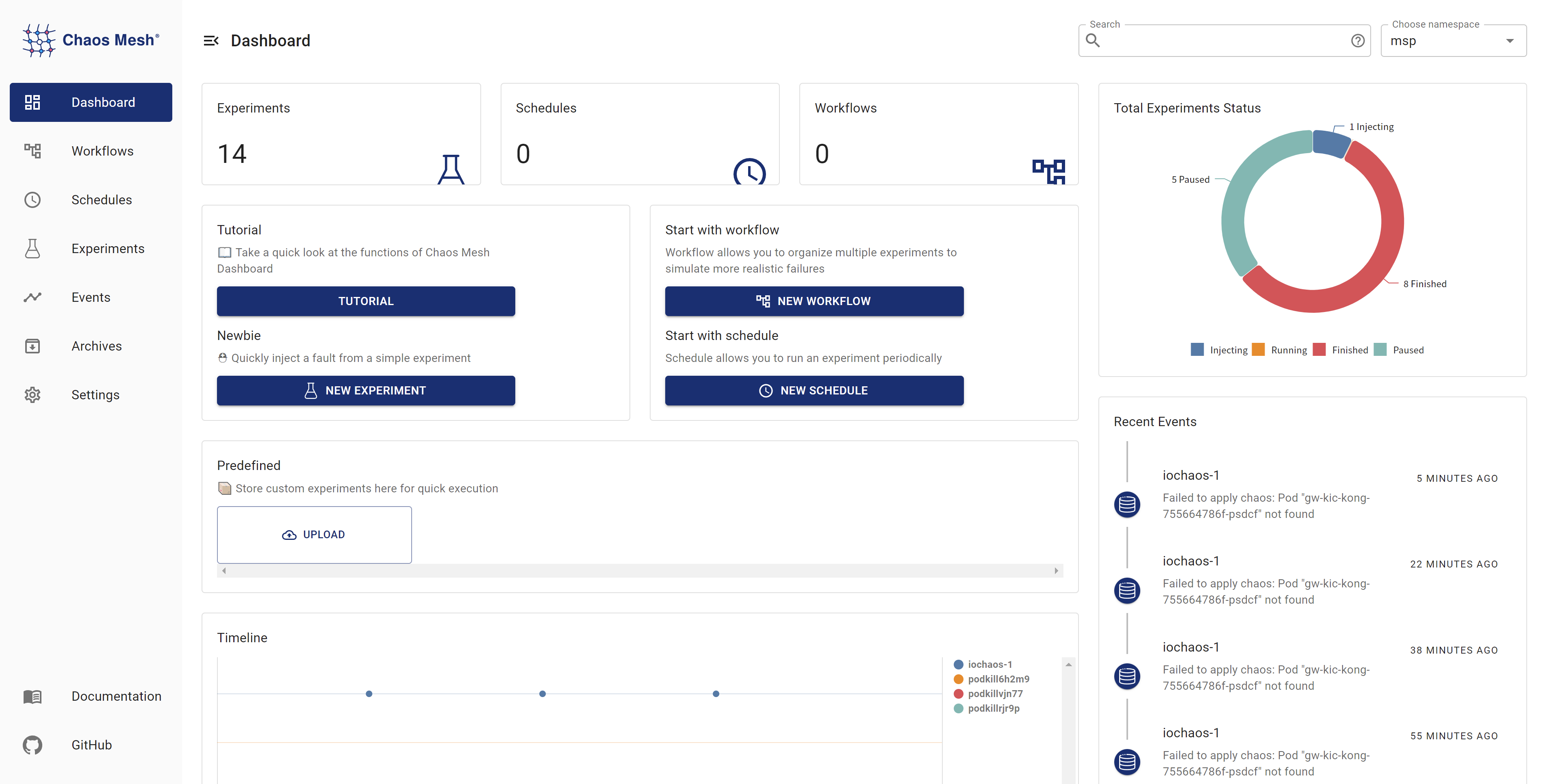
从仪表盘可知平台可能需要实现以下功能:
-
混沌注入
-
Pod 崩溃
-
网络故障
-
负载测试
-
I/O 故障
-
事件追踪
-
关联告警
-
定时遥测
若您对 Chaos Mesh 感兴趣并希望参与改进,欢迎加入 Slack 频道 (#project-chaos-mesh) 或向 GitHub 仓库提交 PR 及 issue。